Requirements
For FSSO to operate correctly it requires:
- The FSSO Collector Agent to be installed on at least one machine monitoring each active domain controller which users are being logged into
- dcagent.dll installed on each active DC
- Correct forward and reverse DNS entries for the workstations clients are connecting from
- Workstations must have Windows remote Registry services started, and it must be accessible from the machine running the FSSO Collector
The FSSO Collector Agent
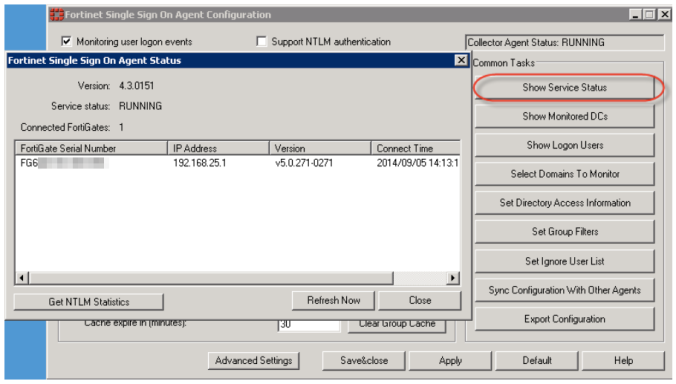
This is the application that collates a view of logged on domain users, and periodically sends this info to the firewall. Only one instance is required but to provide redundancy, the collector can be run on multiple machines. Only one is active at any one time. To locate the active collector, click on the “Show Service Status”. If there is a FortiGate in the list then it is the active FSSO Collector Agent.
FSSO Agent DLL
This is used to interface to the event log on the domain controllers. It is located in C:\Windows\System32\dcagent.dll on each domain controller which is being monitored by a collector.
FSSO Authentication Process
Each collector constantly polls each active domain controller for new eventlog logon events. When a user logs into their workstation, this will generate such an event. The collector will do a reverse lookup on the IP referenced in the eventlog, to verify the user is still logged into their workstation. The collector will then do periodic checks to ensure the user is still active and on the same IP address since the last poll.
These are defined intervals within the FSSO Agent Configuration:
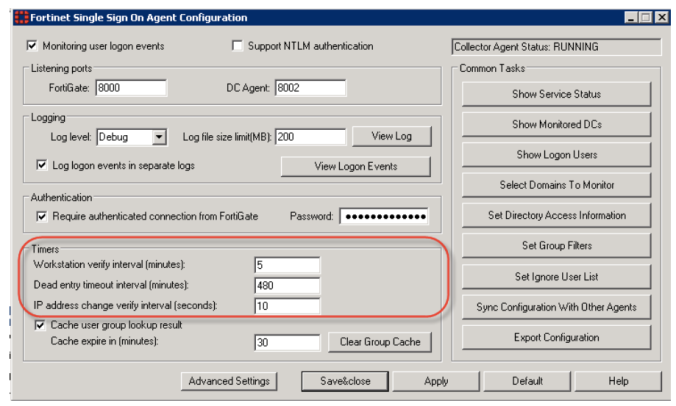
Workstation verify interval
This determines the poll interval for the collector connecting to the workstation (via TCP 139, 445) to verify the user is still logged in. Therefore, the machine which is running the FSSO Collector must have firewall access to the workstations on TCP ports 139 and 445, and the workstation must have remote registry services running.
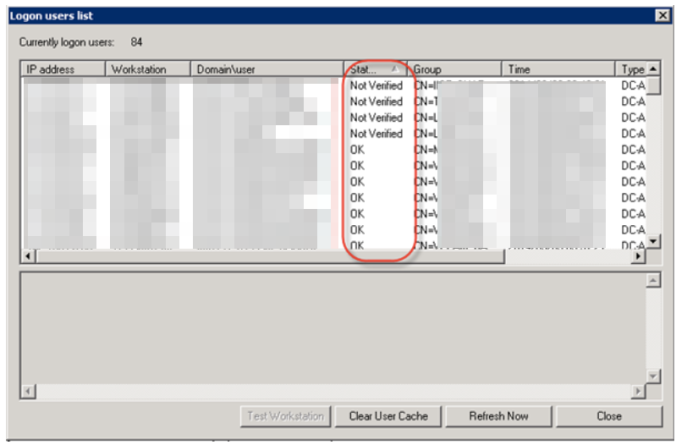
If you look within the “Show logon users” as shown below, you can see the users which are verified with status OK. Where the Status column displays “Not Verified”, this demonstrates that either;-
- The collector hasn’t yet checked to see the user is still logged on
- The machine is still connected but does not have the appropriate ports open or accessible
- The machine is no longer on the network and cannot be communicated with, e.g A laptop has been unplugged from the Ethernet cable and has been taken offsite.
Dead entry timeout interval
At this interval, each of the “Not Verified” user logons (logons found in the eventlog but which the collector is unable to verify by making a remote registry connection to the workstation) present in the collector will be considered dead, and are purged.
IP address change verify interval
This is the period that the FSSO Collector will check to see if the users IP address has changed. This is accomplished by performing a forward lookup on the workstation hostname (the hostname is retrieved from the initial PTR lookup on the IP Address collected from the event log).
Things to note
There are certain circumstances which have been recorded where internet access stops. The two fixes are listed below.
1. The user locks their workstation and unlocks. In most cases this will resolve the issue.
2. If the first does not work. Within command prompt type “ipconfig /registerdns” wait a couple of minute and then try again.
Further investigation is required around a dns register/resolving problem which is resolved by #2.